Strength and conditioning exercises play a crucial role in enhancing swimming performance by improving muscular strength, power, endurance, and overall fitness. Moreover, incorporating a well-rounded strength and conditioning program tailored to swimming-specific needs can help swimmers achieve optimal performance and reduce the risk of injuries. Therefore, understanding recommended exercises and their benefits is essential for developing a comprehensive training regimen.
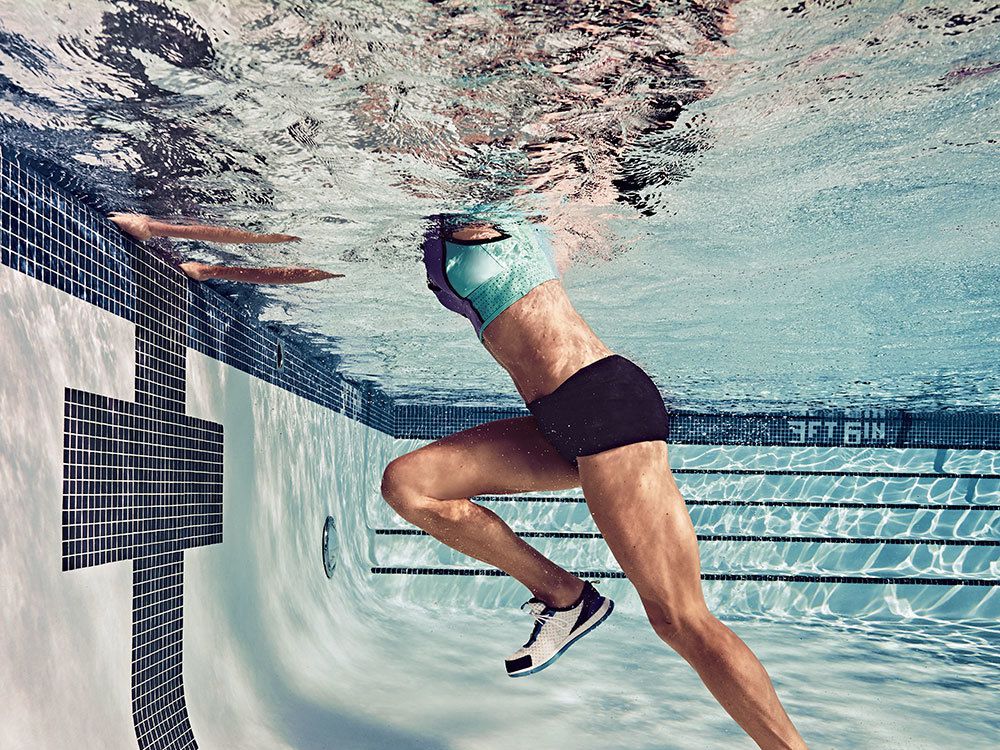

Importance of Strength and Conditioning for Swimmers
Strength and conditioning exercises are vital for swimmers to develop muscular strength and power essential for efficient swimming strokes, starts, turns, and finishes. Moreover, they improve muscle endurance, allowing swimmers to sustain high-intensity efforts throughout races or training sessions. Additionally, strength training helps correct muscle imbalances, enhance joint stability, and prevent overuse injuries common in swimming. Therefore, integrating strength and conditioning into a swimmer’s training program enhances overall physical conditioning and performance.
Core Exercises for Stability and Power
Core exercises are fundamental for swimmers to maintain stability, streamline body positions, and generate power during strokes. Moreover, exercises such as planks, Russian twists, and leg raises target abdominal, oblique, and lower back muscles, improving core strength and stability. Additionally, incorporating exercises that challenge core muscles in multiple planes of movement, such as medicine ball throws and stability ball exercises, enhances overall core strength and coordination. Therefore, prioritizing core exercises improves swimming efficiency and reduces energy expenditure during races.
Lower Body Exercises for Strength and Power
Lower body strength is crucial for swimmers to execute powerful kicks, push-offs from walls, and maintain streamlined body positions. Therefore, strength exercises such as squats, lunges, and deadlifts target major muscle groups in the legs, including quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Moreover, plyometric exercises like box jumps and jump squats improve explosive power and agility, essential for fast starts and turns. Additionally, incorporating resistance band exercises for leg abduction, adduction, and hip flexion strengthens stabilizer muscles and improves joint mobility. Therefore, focusing on lower body exercises enhances leg strength, power, and endurance for improved swimming performance.
Upper Body Exercises for Propulsion and Stability
Upper body strength is critical for swimmers to generate propulsion through strokes, maintain arm and shoulder stability, and reduce fatigue during long-distance swims. Therefore, strength exercises such as pull-ups, lat pulldowns, and bench presses target muscles in the back, shoulders, and arms, improving pulling power and stroke efficiency. Moreover, incorporating swim-specific exercises like resistance band swim strokes and paddle work enhances muscle endurance and replicates swimming motions on dryland. Additionally, shoulder stability exercises such as external rotations and scapular retractions reduce injury risk and improve range of motion. Therefore, integrating upper body exercises enhances arm strength, endurance, and stability for improved swimming performance.
Functional Training and Injury Prevention
Functional training exercises simulate movements and challenges faced during swimming, improving overall athleticism and reducing injury risk. Moreover, exercises such as balance drills on unstable surfaces, agility ladder drills, and single-leg exercises enhance coordination, proprioception, and joint stability. Additionally, incorporating mobility exercises such as dynamic stretches, foam rolling, and yoga promotes flexibility and prevents muscle tightness and injuries. Therefore, prioritizing functional training enhances overall physical readiness and prepares swimmers for the dynamic demands of competitive swimming.
Incorporating Plyometric Training for Power
Plyometric training involves explosive movements that improve muscle power, speed, and agility, essential for competitive swimming performance. Moreover, plyometric exercises such as jump squats, plyo push-ups, and box jumps develop fast-twitch muscle fibers and enhance muscular explosiveness. Additionally, incorporating depth jumps and bounding drills improves reactive strength and jump height, translating to more powerful starts and turns in swimming races. Therefore, integrating plyometric training into a swimmer’s regimen enhances athletic performance and accelerates muscle response time for improved swimming efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recommended strength and conditioning exercises are essential components of a comprehensive training program for swimmers aiming to enhance performance and achieve competitive success. Moreover, incorporating core, lower body, and upper body exercises improves muscular strength, power, endurance, and stability essential for efficient swimming strokes and movements. Additionally, functional training, plyometrics, and injury prevention exercises support overall athleticism and reduce the risk of overuse injuries. Therefore, by prioritizing recommended strength and conditioning exercises, swimmers can optimize their physical conditioning, improve swimming performance, and achieve their goals in the pool.